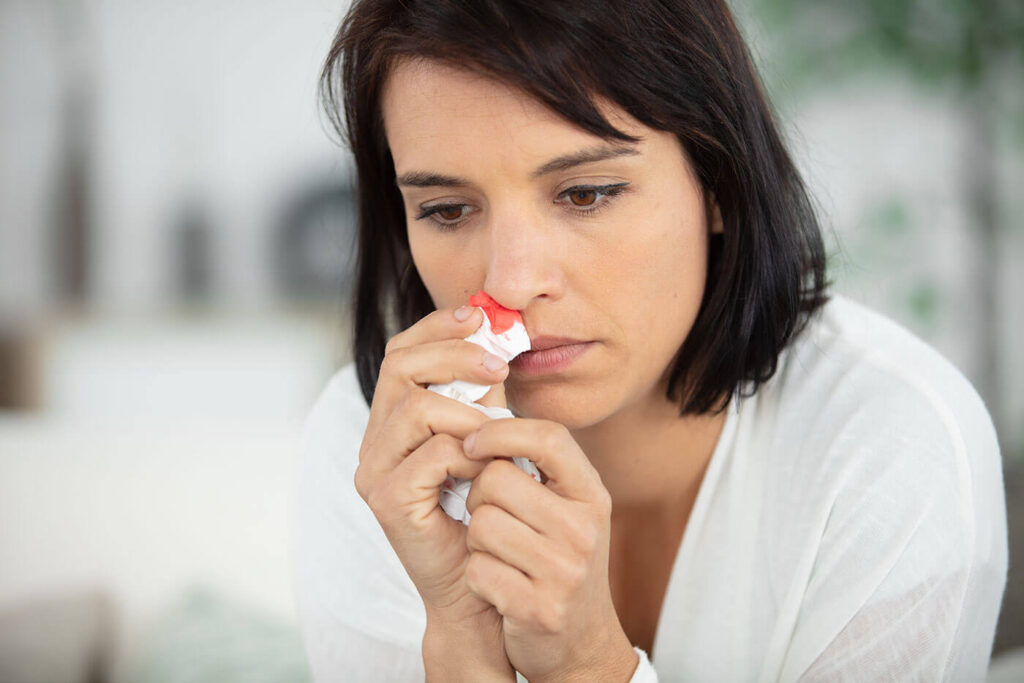
Nosebleeds, also known as epistaxis in medical terms, are actually more common in places like Colorado due to the arid climate. This is because the dry air can irritate and dry out the nasal membranes, making them more prone to cracking and bleeding. This is often experienced by visitors coming to Colorado to recreate in our mountains, especially in the winter.
Nosebleeds Causes
Nosebleeds can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Dry, heated indoor air can dehydrate nasal membranes, causing them to crack, crust and bleed.
- Allergies, colds, or sinus problems: These can cause tissue inflammation.
- Medications: Some medications, such as blood thinners, aspirin, and nasal sprays, can increase the risk of nosebleeds.
- Injury to the nose: Nose picking can cause nosebleeds.
- Anatomic deformities: A deviated septum or vascular malformations can increase the risk of nosebleeds.
Prevention
Try to keep your nose moist when you’re at a higher altitude or drier climates. A saline nasal spray can help. Drinking a lot of water will help prevent your body from dehydrating, too. This can help prevent your nose from drying out and cracking. Using a humidifier at night is an easy way to prevent your nose from drying out. While anyone can experience nosebleeds, they are most common in children between the ages of 2–10 and adults between the ages of 45–65. Nosebleeds can be alarming, but most are not serious and can be treated at home.
Treatment
If you do get a nosebleed while at a high altitude, don’t worry. Treating nosebleeds is the same no matter what altitude you’re at. First, sit upright or lean slightly forward. Firmly pinch your lower nose, below the upper bony part. Use a tissue or, if your nose is bleeding heavily, a paper towel or even a facecloth. Hold your nose for 10-15 minutes. If it continues to bleed, hold it for another 10-15 minutes. If you need help stopping the bleeding, an over-the-counter nasal spray could help If the bleeding doesn’t stop, or if you think you or your child needs to see a doctor, you should call your doctor.
Disclaimer: This is general information and not a substitute for professional medical advice. All advice and suggestions offered via the website or newsletters should be discussed with a physician prior to being implemented. Always consult a physician for specific guidance, especially if you have any pre-existing conditions. SurgOne, PC and ENTOne, PC are not liable for any adverse reactions that may occur by implementing advice or suggestions that appear here.